树莓派RP2350-桌面动态温湿度计
1 树莓派RP2350-桌面动态温湿度计
本文介绍了DFRobot Beetle RP2350开发板结合DHT11模块、锂电池模块、随机眨眼动画,实现OLED 显示的桌面动态温湿度计的项目设计。
2 项目介绍
本项目包括如下。
工作原理:ADC电压采集与电量转换
工程调试:电量获取、电量图标显示、DHT11温湿度显示、OLED眨眼动画
工程代码:合并调试代码,实现完整的项目设计功能
效果演示:帧动画显示、动态展示
最终实现桌面动态温湿度计的制作。
3 工作原理
根据开发板原理图可知,电池VBAT的分压电路与主控的GPIO29模拟接口相连,因此通过该引脚可实时采集监测电池电压信息,进而实现电量显示。
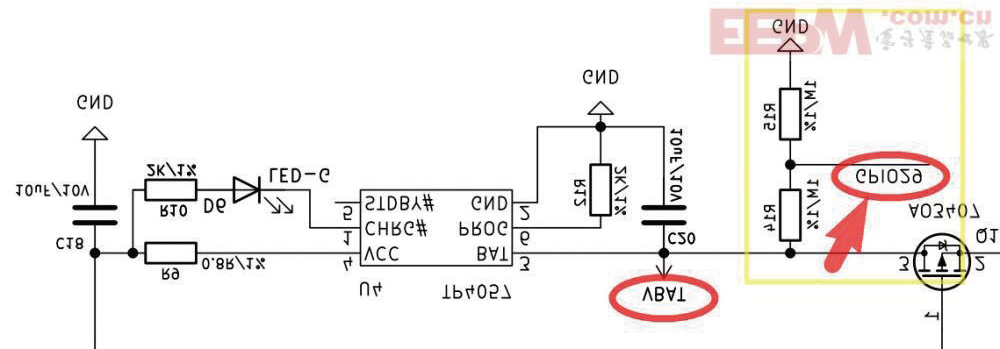
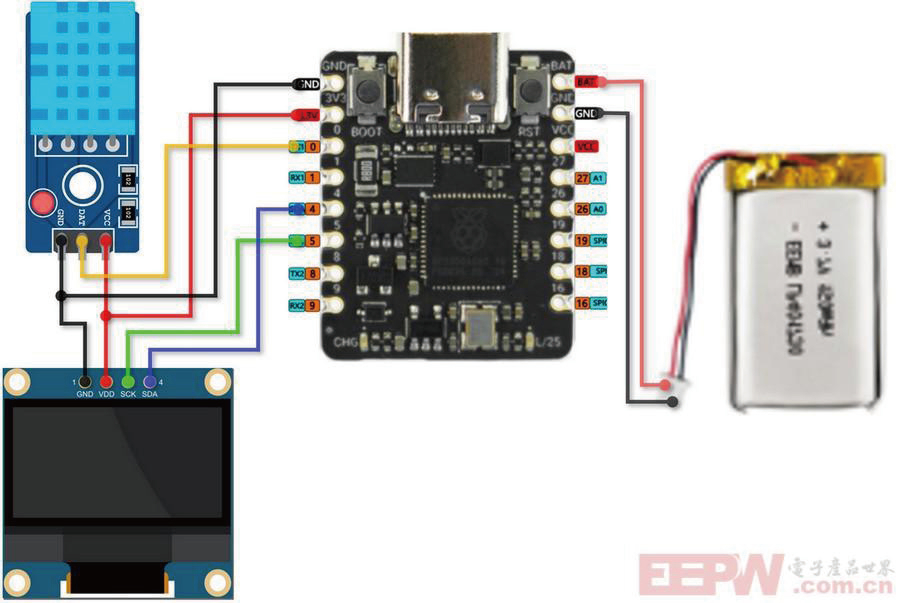
4 硬件连接
GP0->DATA(DHT11)
GP4->SDA(OLED)
GP5->SCL(OLED)
BAT->Battery Positive
GND->Battery Negative
5 示意图
6 工程调试
包括ADC电量采集、电量的OLED显示、DHT11温湿度数据和电量图标的显示、眨眼动画等调试项目。
7 电量获取
通过ADC 读取GPIO29 电压值并终端打印
8 代码
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
1.from machine import Pin, ADC
2.import utime
3.
4.#initialize ADC pin
5.adc = ADC(Pin(29))
6.
7.#parameters for voltage divide resistor
8.R1, R2=1000000, 1000000
9.DIV_RATIO=(R1 + R2)/R1
10.
11.def get_battery_level():
12.adc_value = adc.read_u16()
13.voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
14.actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
15.percent=min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) / (4.2-3.3) *100, 0), 100)
16.return percent, actual_voltage
17.
18.while True:
19. percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
20. print(‘Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level: {:.1f}%’.format(voltage,percent))
21. utime.sleep(1)
保存代码,连接开发板,配置解释器并运行。
9 效果
终端打印ADC 采集的电池电压值以及电量百分比
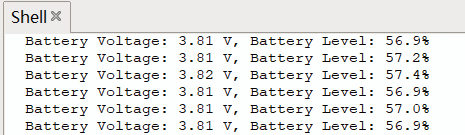
10 电量显示
OLED显示ADC采集的电量百分比。
11 代码
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
1.from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
2.import ssd1306
3.import utime
4.
5.#initialize ADC pin
6.adc=ADC(Pin(29))
7.
8.#initialize OLED
9.i2c=I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
10.oled=ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
11.
12.#parameters of voltage divide resistor
13.R1, R2=1000000, 1000000 # 1M
14. Vref_BAT=3.9#battery voltage in full charged state
15.
16.def get_battery_level():
17. adc_value = adc.read_u16()
18. voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
19. DIV_RATIO = (R1 + R2) / R1
20. actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
21. percent=min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) /(Vref_BAT - 3.3) * 100, 0), 100)
22. return percent, actual_voltage
23.
24.def draw_battery(percent):
25. oled.fill(0)
26. oled.text(‘{:.0f}%’.format(percent), 0, 17)
27. # draw battery cartoon icon
28. oled.rect(0, 0, 30, 15, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
29. oled.rect(30, 5, 3, 5, 1) # anode
30. oled.fill_rect(2, 2, int(26 * percent / 100), 11, 1) # electric percent column
31. oled.rotate(0)
32. oled.show()
33.
34.def BAT_display(percent,x,y): # battery percent,icon position (x,y)
35. oled.fill(0)
36. oled.text(‘{:.0f}%’.format(percent), 0+x, 17+y)
37. # draw battery cartoon icon
38. oled.rect(0+x, 0+y, 30, 15, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
39. oled.rect(30+x, 5+y, 3, 5, 1) # anode
40. oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2+y, int(26 * percent / 100),11, 1) # electric percent column
41. oled.rotate(0)
42. oled.show()
43.
44.def draw_vertical_battery(percent,x,y): # battery percent, icon position (x,y)
45. oled.fill(0)
46. oled.text(‘{:.0f}’.format(percent), 0+x, 33+y)
47. # draw battery cartoon icon
48. oled.rect(0+x, 2+y, 15, 30, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
49. oled.rect(5+x, 0+y, 5, 3, 1) # anode
50. fill_h = int(27 * percent / 100)
51. oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2 + (28 - fill_h) + y, 11, fill_h, 1) # percent column
52. oled.rotate(0)
53. oled.show()
54.
55.while True:
56. percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
57. #draw_battery(percent)
58. BAT_display(percent,90,2)
59. #draw_vertical_battery(percent,90,9)
60. print(‘Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level:{:.1f}%’.format(voltage,percent))
61. utime.sleep(2)
保存代码,连接开发板,配置解释器并运行。
12 效果
电量图标的水平显示
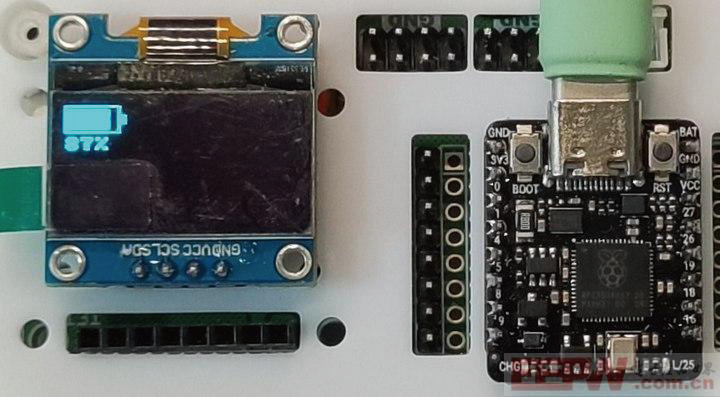
电量图标的竖直显示
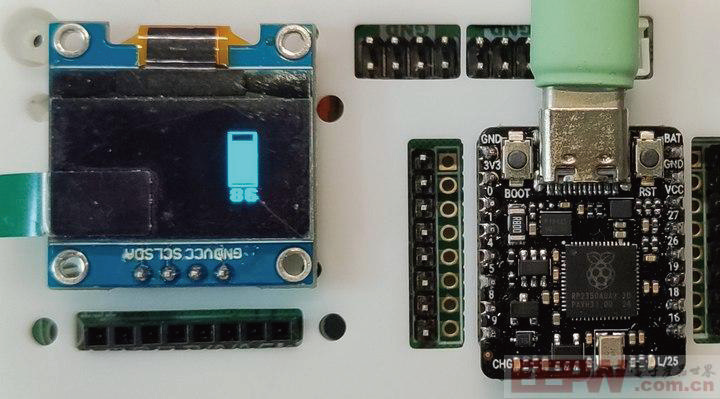
13 DHT11温湿度计
带电量显示的DHT11温湿度计
14 代码
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
1.from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
2.from PicoDHT22 import PicoDHT22
3.import ssd1306
4.import utime
5.
6.#initialize ADC pin
7.adc = ADC(Pin(29))
8.
9.#initialize OLED
10.i2c=I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
11.oled=ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
12.
13.#parameters of voltage divide resistor
14.R1, R2 = 1000000, 1000000
15.Vref_BAT = 3.81 # battery voltage in full charged state
16.
17.def get_battery_level():
18. adc_value = adc.read_u16()
19. voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
20. DIV_RATIO = (R1 + R2) / R1
21. actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
22. percent = min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) /(Vref_BAT - 3.3) * 100, 0), 100)
23. return percent, actual_voltage
24.
25.def draw_battery(percent):
26. oled.fill(0)
27. oled.text(‘{:.0f}%’.format(percent), 90, 27)
28. # draw battery cartoon icon
29. oled.rect(90, 10, 30, 15, 1) # frame
30. oled.rect(120, 15, 3, 5, 1) # anode
31. oled.fill_rect(92, 12, int(26 * percent / 100),11, 1) # electric percent column
32. oled.show()
33.
34.def BAT_display(percent):
35. oled.fill(0)
36. oled.text(‘{:.0f}%’.format(percent), 90, 27)
37. # draw battery cartoon icon
38. oled.rect(90, 10, 30, 15, 1) # frame
39. oled.rect(120, 15, 3, 5, 1) # anode
40. oled.fill_rect(92, 12, int(26 * percent / 100), 11, 1)
41. oled.show()
42.
43.def draw_vertical_battery(percent,x,y):
44. #局部清屏并显示电量百分比
45. oled.fill_rect(x,y,15+8,30+16,0)
46. oled.text(‘{:.0f}’.format(percent), 0+x, 33+y)
47. #竖版电池绘制
48. oled.rect(0+x, 2+y, 15, 30, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
49. oled.rect(5+x, 0+y, 5, 3, 1) # anode
50. fill_h = int(26 * percent / 100)
51. oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2 + (28 - fill_h) + y, 11, fill_h, 1) # percent column
52. oled.rotate(0)
53. oled.show()
54.
55. def display_TH(temp,humi):
56. oled.fill_rect(20,15,6*8,64-15,0) #局部清屏
57. oled.text(“Temperature:”, 0, 0)
58. oled.text(“{:.1f} C”.format(temp), 20, 15)
59. oled.text(“Humidity:”, 0, 35)
60. oled.text(“{:.1f} %”.format(humi), 20, 50)
61. oled.rotate(0) # rotate the screen display for a more comfortable position
62. oled.show()
63.
64.dht_sensor=PicoDHT22(Pin(0,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP),dht11=True)
65.while True:
66. temp,humi = dht_sensor.read()
67. percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
68. #draw_battery(percent)
69. #BAT_display(percent)
70. draw_vertical_battery(percent,90,16)
71. display_TH(temp,humi)
72. print(‘Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level:{:.1f}%’.format(voltage,percent))
73. utime.sleep(2)
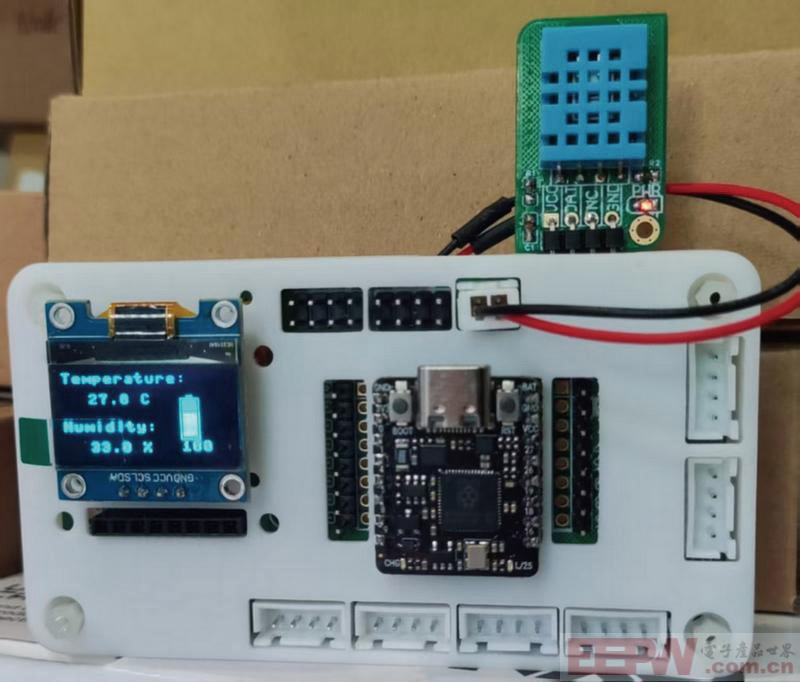
15 效果
电量和温湿度显示,数据刷新的时间间隔为2秒
16 眨眼动画
OLED显示矩形填充状眼睛,改变形状并利用人眼的视觉暂留效应实现眨眼效果。
17 代码
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
1.from machine import Pin, I2C
2.import ssd1306
3.import utime
4.import urandom
5.
6.i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
7.oled_width = 128
8.oled_height = 64
9.oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c)
10.
11.def draw_eyes(state,xshift,yshift):
12. “””state: 0=完全睁开, 1=半闭, 2=完全闭上”””
13. width,height = (int)(oled_width/5),(int)(oled_height/3)
14. cx,cy=(int)((oled_width-2.5*width)/2),(int)((oled_height-height)/2) # eyes at scrren center 定位点为矩形左上角
15. x=cx+xshift
16. y=cy+yshift
17. oled.fill_rect(x, y, int(2.5*width), height, 0)
18. #draw left eye
19. if state == 0: # 完全睁开
20. oled.fill_rect(x, y, width, height, 1)
21. elif state == 1: # 半闭
22. oled.fill_rect(x, y+(int)(height/4), width,(int)(height/2), 1)
23. else: # 完全闭上
24. oled.hline(x, y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
25. # draw right eye
26. if state == 0: # 完全睁开
27. oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y, width, height, 1)
28. elif state == 1: # 半闭
29. oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/4), width, (int)(height/2), 1)
30. else: # 完全闭上
31. oled.hline(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
32. oled.show()
33.
34.def blink_eyes(xshift,yshift):
35. #睁眼状态保持
36. draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift)
37. utime.sleep(1)
38. #眨眼动画序列
39. draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # 半闭
40. utime.sleep(0.1)
41. draw_eyes(2,xshift,yshift) # 全闭
42. utime.sleep(0.1)
43. draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # 半闭
44. utime.sleep(0.1)
45. draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift) # 全开
46.
47.def random_eyes():
48. xshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_width/4),(int)(oled_width/4))
49. yshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_height/3),(int)(oled_height/3))
50. oled.fill(0)
51. blink_eyes(xshift,yshift)
52. #print(xshift,yshift)
53.
54.while True:
55. random_eyes()
56. #blink_eyes(0,0)
保存代码,连接开发板,配置解释器并运行。
18 效果
眨眼效果(眼睛位置在屏幕内随机移动)

19 工程代码
将工程调试的代码合并,实现温湿度数据(包括电池电量)与息屏随机眨眼动画的切换显示。
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
1.from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
2.from PicoDHT22 import PicoDHT22
3.import ssd1306
4.import utime
5.import urandom
6.
7.#initialize ADC pin
8.adc=ADC(Pin(29))
9.
10.#initialize OLED
11.i2c=I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
12.oled_width=128
13.oled_height=64
14.oled=ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c)
15.
16.#parameters of voltage divide resistor
17.R1, R2=1000000, 1000000
18.Vref_BAT=3.81 # battery voltage in full charged state
19.
20.def get_battery_level():
21. adc_value=adc.read_u16()
22. voltage=(adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
23. DIV_RATIO=(R1+R2)/R1
24. actual_voltage=voltage*DIV_RATIO#voltage division compensation
25. percent=min(max((actual_voltage-3.3) /(Vref_BAT-3.3) *100, 0),100)
26. return percent, actual_voltage
27.
28.def draw_vertical_battery(percent,x,y):
29. # 局部清屏并显示电量百分比
30. oled.fill_rect(x,y,15+8,30+16,0)
31. oled.text(‘{:.0f}’.format(percent), 0+x, 33+y)
32. # 竖版电池绘制
33. oled.rect(0+x, 2+y, 15, 30, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
34. oled.rect(5+x, 0+y, 5, 3, 1) # anode
35. fill_h=int(26 * percent / 100)
36. oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2 + (28 - fill_h) + y, 11, fill_h, 1) # percent column
37. oled.rotate(0)
38. oled.show()
39.
40.def display_TH(temp,humi):
41. oled.fill_rect(20,15,6*8,64-15,0) # part clear
42. oled.text(“Temperature:”, 0, 0)
43. oled.text(“{:.1f} C”.format(temp), 20, 15)
44. oled.text(“Humidity:”, 0, 35)
45. oled.text(“{:.1f} %”.format(humi), 20, 50)
46. oled.rotate(0) # rotate the screen display for a more comfortable position
47. oled.show()
48.
49.def draw_eyes(state,xshift,yshift):
50. “””state: 0=full open, 1=half open, 2=close”””
51. width,height = (int)(oled_width/5),(int)(oled_height/3)
52. cx,cy = (int)((oled_width-2.5*width)/2),(int)((oled_height-height)/2) # eyes at scrren center
53. x=cx+xshift
54. y=cy+yshift
55. oled.fill_rect(x, y, int(2.5*width), height, 0)
56. #draw left eye
57. if state==0: # full open
58. oled.fill_rect(x, y, width, height, 1)
59. elif state == 1: # half open
60. oled.fill_rect(x, y+(int)(height/4), width,(int)(height/2), 1)
61. else: # close
62. oled.hline(x, y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
63. #draw right eye
64. if state==0: # full open
65. oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y, width, height, 1)
66. elif state == 1: # half open
67. oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/4), width, (int)(height/2), 1)
68. else: # close
69. oled.hline(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
70. oled.show()
71.
72.def blink_eyes(xshift,yshift):
73. #keep opening
74. draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift)
75. utime.sleep(0.5)
76. # blink eyes order
77. draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # half open
78. utime.sleep(0.1)
79. draw_eyes(2,xshift,yshift) # close
80. utime.sleep(0.1)
81. draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # half open
82. utime.sleep(0.1)
83. draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift) # full open
84. utime.sleep(0.5)
85.
86.def random_eyes():
87. xshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_width/4),(int)(oled_width/4))
88. yshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_height/3),(int)(oled_height/3))
89. oled.fill(0)
90. blink_eyes(xshift,yshift)
91. #print(xshift,yshift)
92.
93.dht_sensor = PicoDHT22(Pin(0,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP),dht11=True)
94.def TH_BAT():
95. ‘’’ temperature and humidity and battery ‘’’
96. temp,humi = dht_sensor.read()
97. percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
98. oled.fill(0)
99. display_TH(temp,humi)
100. draw_vertical_battery(percent,90,16)
101. print(‘Temperature: {:.2f} C, Humidity: {:.2f} RH, Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level:{:.1f}%’.format(temp,humi,voltage,percent))
102. utime.sleep(2)
103.
104.while True:
105. TH_BAT()
106. random_eyes()
连接开发板,配置解释器,将代码保存至根目录,取下数据线,连接电池,实现显示效果。
20 效果
帧动画分别如下
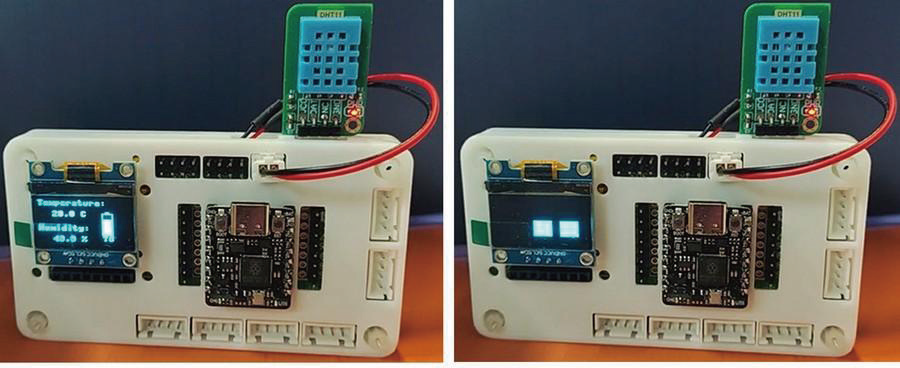
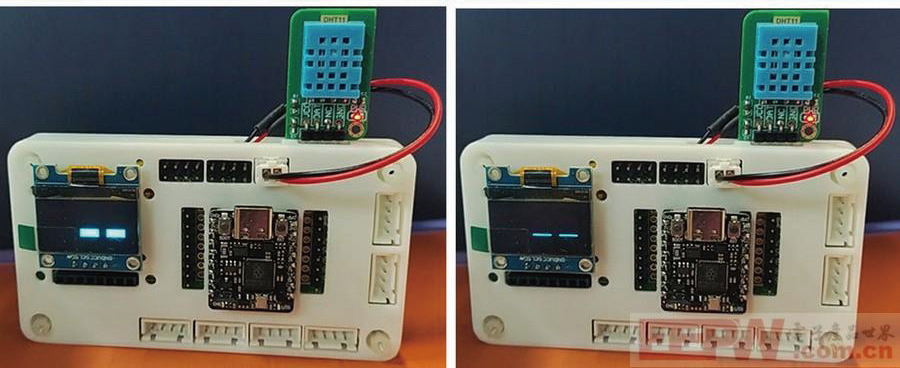
21 总结
本文介绍了树莓派RP2350开发板结合DHT11模块、锂电池模块、随机眨眼动画,实现OLED显示的桌面动态温湿度计的项目设计。通过多任务结合,为更多DIY设计提供了可能,如添加按键扫描或语音控制模块,实现指定的功能切换与人机交互,拓展和丰富了该开发板在物联网领域的创新与应用,为RP2350 的开发设计和产品应用提供了参考。
(本文来源于《EEPW》202506)

加入微信
获取电子行业最新资讯
搜索微信公众号:EEPW
或用微信扫描左侧二维码